Starting a new semester as second year student is quite tough with phisiology of microbe where i will learn about the metabolism involved in the microbes . the first chapter we recall the structures of the prokaryotes that we already learn in last semester.have you still remember what is prokaryotes ?
What is prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes consist of bacteria and archea that lack or nucleus, or membrane bounded
organelles,most unicellular but myxobacter have multicellular life cycle.
- · Bacteria(cell wall with muramic acid,membrane-ester-linkage,lipid bilayer,thymidine in tRNA)
- · Archaea(cell wall w/o muramic acid,membrane-ether-linkage,lipid monolayer,w/o thymidine in tRNA)
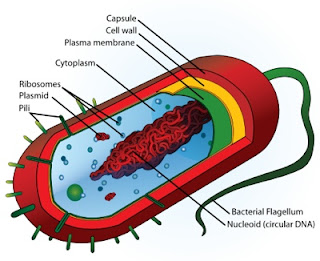
this is cell structure of procaryote
here is the function of the cell structure
1)capsule-additional cover that protect cell
when it is engulf by another organism, moisture help to adhere to surface and
nutrient
2)cell wall-protect the bacteria and give
shape
3)cytoplasm-gel like structure mainly of
water contain enzyme, salt, cell component, various organic molecule
4)plasma membrane- regulate the flow of
substance in and out of cell
5)pili, fimbriae-hair like structure on the
surface of cell, attach to another bacteria cell, help attachment
6)flagella-locomotion
7)ribosome-synthesis protein
8)plasmid-carrying gene, circular DNA
My friends and i were asked by Dr Wan to do some research about the types of proteobacteria. Proteobacteria is the largest division of bacteria.
It consist of 6 main groups which are:-
More information about these proteobacteria can be refered by this link below :
It consist of 6 main groups which are:-
1. Epsilon
2. Delta proteobacteria
3. Gamma proteobacteria
4. Beta proteobacteria
5. Alpha proteobacteria
6. Zeta proteobacteria More information about these proteobacteria can be refered by this link below :
I enjoyed learned this topic as i can remember the first semester topic as the structures of the Prokaryotes are very important in order to be easier for us to understand the further topics.
No comments:
Post a Comment